Nickel is a white metal, with a faint tinge of yellow. It is used widely in making alloys, including copper-nickel (75% copper, 25% nickel) which is used in coinage.

Nickel is used in the production of the strongly ferromagnetic alloy alnico which is used to make strong permanent magnets. Alnico alloys iron, nickel, cobalt and aluminum.

Stainless steel contains 12-18% chromium and usually about 8% nickel.
This is a list of chemical elements, sorted by atomic mass (or most stable isotope) and color coded according to type of element. Each element's atomic number, name, element symbol, and group and period numbers on the periodic table are given. The number in parenthesis gives the uncertainty in the 'concise notation' dis given in parenthesis next to the least significant digits to which it. Symbol: Ni Atomic Number: 28 Atomic Mass: 58.6934 amu Melting Point: 1453.0 °C (1726.15 K, 2647.4 °F) Boiling Point: 2732.0 °C (3005.15 K, 4949.6 °F) Number of Protons/Electrons: 28 Number of Neutrons: 31 Classification: Transition Metal Crystal Structure: Cubic Density @ 293 K: 8.902 g/cm 3 Color: white Atomic Structure.
Iron objects can be plated with nickel for corrosion resistance.
Mass of Atom (u)% Abundance 57 Fe 56.935399 2.119 58 Fe 57.933280 0.282 27 Cobalt 59 Co 58.933200 100 28 Nickel 58 Ni 57.9353 60 Ni 59.9307 61 Ni 60.931060 1.1399 62 Ni 61.928349 3.6345 64 Ni 63.927970 0.9256 29 Copper 63 Cu 62.929601 69.17 65 Cu 64.927794 30.83 30 Zinc 64 Zn 63.929147 48.63. Molecular mass (molecular weight) is the mass of one molecule of a substance and is expressed in the unified atomic mass units (u). (1 u is equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12) Molar mass (molar weight) is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in g/mol. Weights of atoms and isotopes are from NIST article. It provides atomic mass, mass excess, nuclear binding energy, nucleon separation energies, Q-values, and nucleon residual interaction parameters for atomic nuclei of the isotope Ni-92 (Nickel, atomic number Z = 28, mass number A = 92).
The principal ores of nickel are nickelite (NiAs), millerite (NiS), and pentlandite ((Ni,Fe)S. Nickel forms a sulfide mineral with arsenic called gersdorffite. Nickel forms another arsenide called nickel-skutterudite, NiAs2-3. The sulfide formed with antimony is called ullmannite. Copper, cobalt and nickel join in the sulfide carrollite, Cu(Co,Ni)2S4. Cobalt and nickel form the sulfide siegenite, CoNi2S4. Nickel is often found in association with iron and sometimes forms the compound Ni3Fe, called awaruite in its mineral form. Nickel-iron meteorites are fairly common. A major source of nickel is the Sudbury Basin in Canada associated with the second largest meteoritic impact crater on the Earth.
Nickel is used in alloy with gold to make 'white gold' for jewelry use.
| Atomic data | Nuclear data |
| Atomic Structure | |
|---|---|
| Symbol | Ni |
| Atomic Number | 28 |
| Atomic Mass | 59 g/mol |
| Periodic Table | |
| Group | 10 |
| Row / Period | 4 |
| Element Category | Transition dhaatu |
| Chhapa | |
Nickel ke electron shell | |
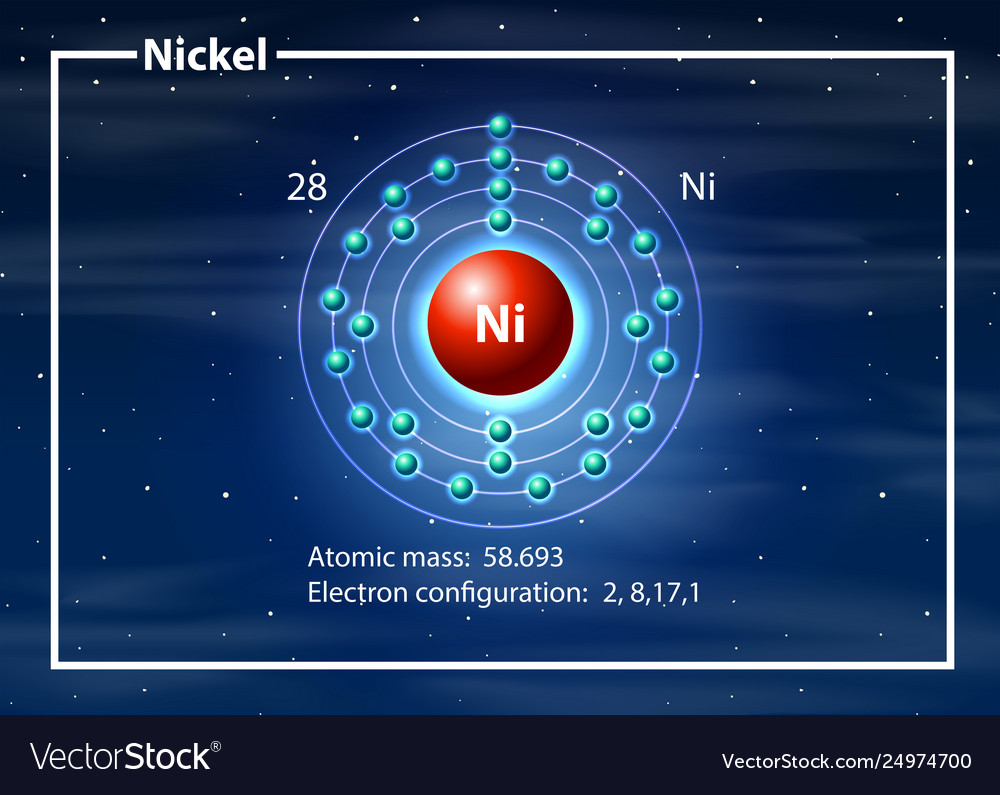

Nickel (chemical symbolNi) ek chemical element hae jiske atomic number 28 aur atomic mass 59 hae. Ii ek transition metal hae.
No Atomic Mass
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Atomic Mass Example




